In our daily life, we use many electronic gadgets and machines. All of them require a stable and fixed voltage to work properly. If the voltage keeps changing, these devices may stop working or even get damaged. That’s where a regulated power supply comes in. No matter how much the input voltage changes, it provides a constant and stable voltage. Let’s understand this topic in a simple way.
What is a Regulated Power Supply?
A regulated power supply is a device or circuit that provides a constant output voltage. It does this by controlling and adjusting to changes in the input voltage or load. Even if the input power goes up or down, the output remains the same. This helps protect sensitive electronic components.
For example, your mobile phone charger provides a 5V output. Even if the voltage in your home is slightly lower or higher, your phone gets a fixed 5V. That charger is a type of regulated power supply.
Why do we need it?
Electricity from the mains power supply is not always constant. The voltage can fluctuate or decrease. Most electronic circuits require a fixed voltage to run smoothly. If the voltage gets too high or too low, it can damage or even destroy the device.
A regulated power supply ensures that the voltage remains at the right level. This helps to:
- Protect devices
- Improve performance
- Extend the life of electronic components
Main parts of a regulated power supply
Let’s look at the basic components used to make a regulated power supply:
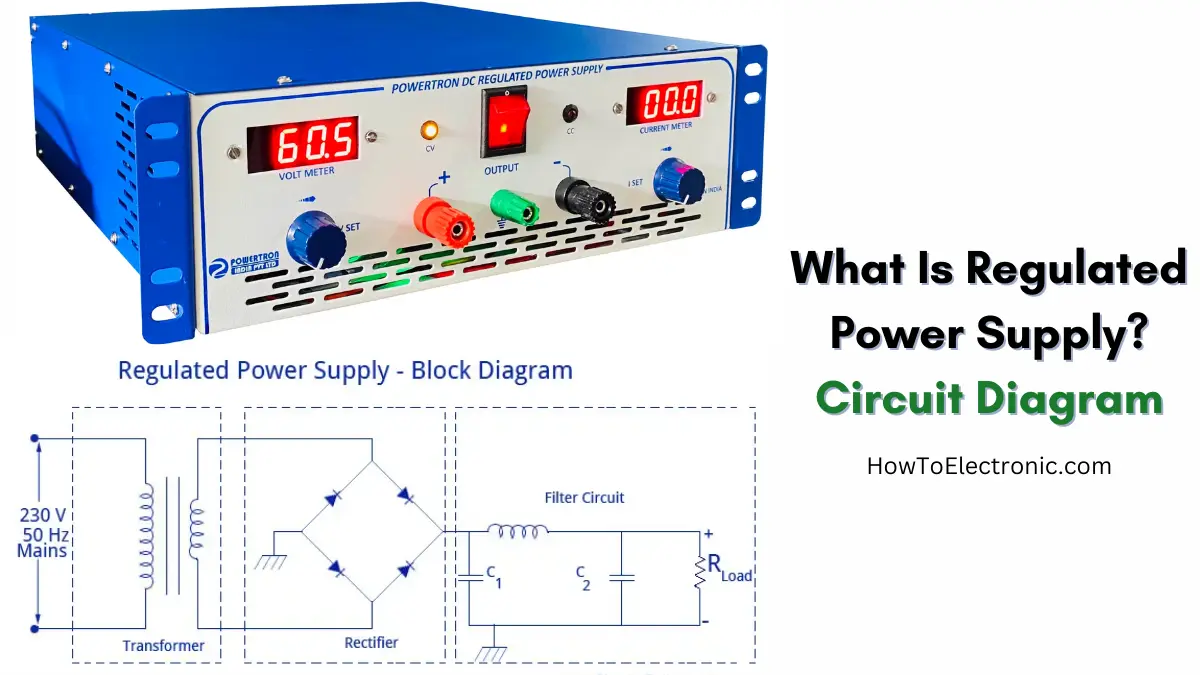
Transformer:
It changes the high voltage from the mains to a low voltage. It also isolates the power supply from the mains for safety.
Rectifier:
It converts AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current). Usually, we use diodes in a bridge formation to do this.
Filter:
The rectifier gives a DC that still has ripples (small AC parts). The filter smooths out these ripples. Capacitors are mostly used here.
Voltage regulator:
This is the main part. It keeps the output voltage constant even if the input or load changes. It can be made using components like zener diodes, transistors or IC regulators like 7805.
Circuit Diagram
Here is a simple layout of a basic regulated power supply:
- The transformer steps down 230V AC to 12V AC.
- The rectifier converts the 12V AC to 12V DC (but with ripples).
- The filter smooths out the ripples and gives clean DC.
- The voltage regulator ensures that the final output remains at 5V, 9V, or 12V, as required.
How does it work?
A regulated power supply works in stages:
Voltage step down:
The transformer steps down the high AC voltage to a safe level.
AC to DC conversion:
The rectifier uses diodes to allow current to flow in only one direction, converting AC to DC.
Filtering:
The DC from the rectifier still fluctuates. Capacitors are used to reduce these fluctuations and smooth out the voltage.
Regulation:
A voltage regulator regulates the output. It adjusts and keeps the voltage constant even if the input or load changes.
Types of Regulated Power Supplies
Linear Power Supply:
It uses a transformer, rectifier, filter, and linear voltage regulator. It is simple and gives a clean output, but it can be heavy and generate heat.
Switching Power Supply (SMPS):
It works with high-frequency switching. It is more efficient and lighter but can be a bit complex and noisy.
Benefits
- Provides stable voltage
- Protects sensitive electronics
- Reduces electrical noise and ripple
- Extends the life of equipment
Uses of regulated power supplies
Regulated power supplies are used in many places where a stable voltage is important. Some common uses include:
Mobile chargers:
They convert AC to a fixed DC voltage such as 5V or 9V.
Computers and laptops:
The internal power supply keeps all components running at a fixed voltage.
Medical devices:
Devices such as ECGs or heart monitors require a stable power supply for accurate results.
Laboratories:
Laboratory equipment requires a specific voltage for testing and research.
Telecommunications systems:
Networking devices and telephone systems rely on a constant voltage.
Embedded Systems and Microcontrollers:
These small devices require a specific voltage level for proper operation.
Industrial Machines:
Machines with sensors, controllers, and processors must receive the correct voltage to avoid failure.
Final Words
Regulated power supplies play a key role in the world of electronics. Be it a small gadget or a large machine, all require a fixed voltage to function smoothly. From mobile chargers to industrial equipment, regulated power supplies help them run safely and efficiently. By providing a consistent voltage, it protects valuable electronics and improves their performance. In short, for any reliable electronic system, regulated power supplies are the backbone.